介绍
树
–》二叉树
–》–》完全二叉树
–》–》–》满二叉树

完全二叉树高度:h = logN + 1
满二叉树高度:h = log(N+1)

OJ
1.单值二叉树
如果二叉树每个节点都具有相同的值,那么该二叉树就是单值二叉树。
只有给定的树是单值二叉树时,才返回 true;否则返回 false。
示例 1:
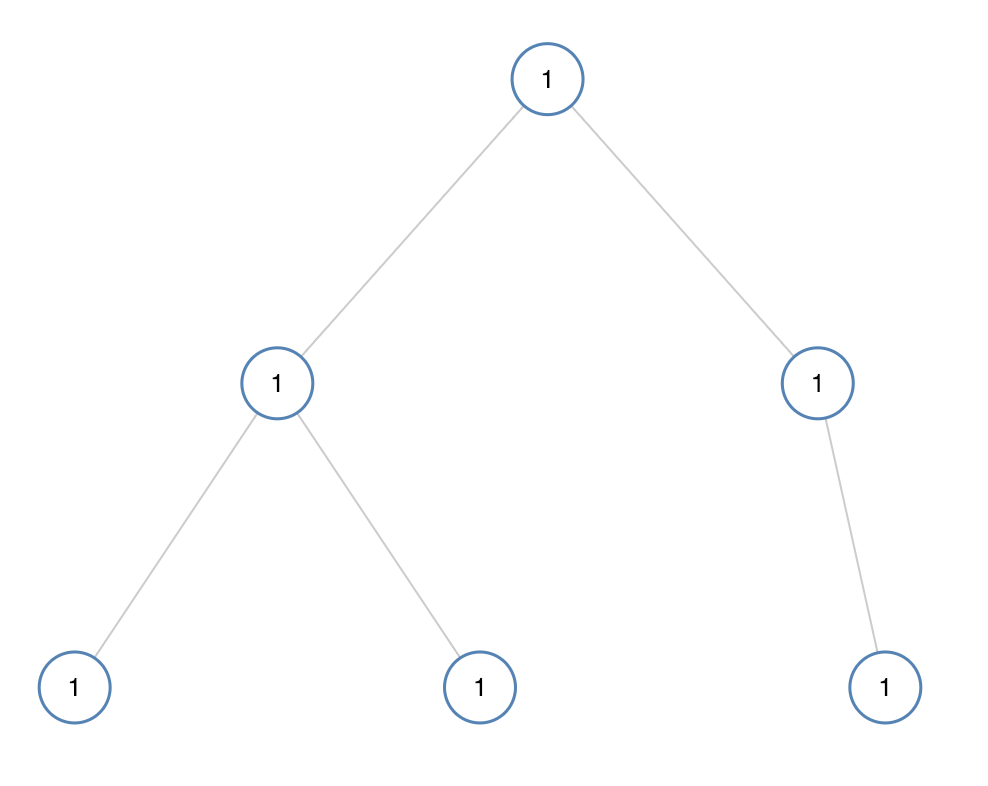
输入:[1,1,1,1,1,null,1]
输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(root->left&& root->val != root->left->val)
return false;
if(root->right&& root->val != root->right->val)
return false;
return isUnivalTree(root->left)&&isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
2.二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return left>right? left+1:right+1;
}
3.翻转二叉树
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root,请左右翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
示例 1:
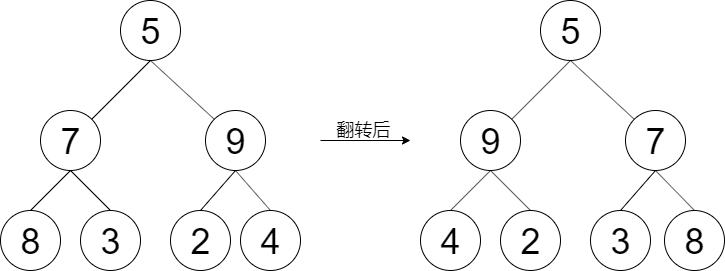
输入:root = [5,7,9,8,3,2,4]
输出:[5,9,7,4,2,3,8]
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
// struct TreeNode* flipTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
// if(root == NULL)
// {
// return NULL;
// }
// struct TreeNode* left = root->left;
// root->left = root->right;
// root->right = left;
// flipTree(root->left);
// flipTree(root->right);
// return root;
// }
//法二
struct TreeNode* flipTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct TreeNode* left = flipTree(root->left);
root->left = flipTree(root->right);
root->right = left;
return root;
}
4.相同的树
给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。
如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
示例 1:
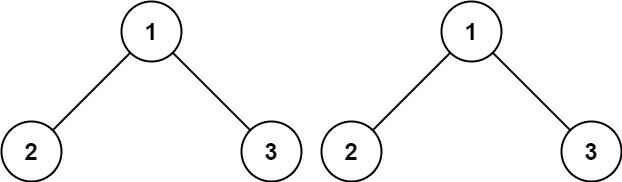
输入:p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
//结束条件
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
return true;
//结构上
if(p==NULL&&q!=NULL)
return false;
if(p!=NULL&&q==NULL)
return false;
if(p->val!=q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
5.对称二叉树
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
示例 1:
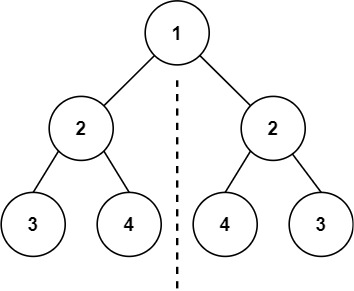
输入:root = [1,2,2,3,4,4,3]
输出:true
示例 2:
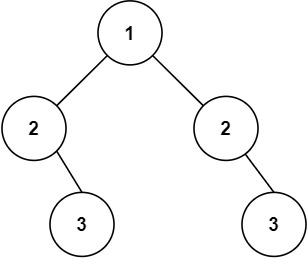
输入:root = [1,2,2,null,3,null,3]
输出:false
算法思路:从第一层开始判断左右子树的结构是否对称,然后以第二层左右结点为根,判断其两个子树左右结构上是否相同,结构相同判断结点值是否相同,依次往下判断第三第四层,当左右结点都为空表示结束。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
typedef struct TreeNode Node;
bool _isSymmetric(Node* root1,Node* root2)
{
if(root1==NULL&&root2==NULL)
return true;
//结构上
if(root1!=NULL&&root2==NULL)
return false;
if(root1==NULL&&root2!=NULL)
return false;
//结点值上
if(root1->val != root2->val)
return false;
if(_isSymmetric(root1->left,root2->right)&&_isSymmetric(root1->right,root2->left))
return true;
return false;
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root) {
return _isSymmetric(root->left,root->right);
}
6.另一个树的子树
给你两棵二叉树 root 和 subRoot 。检验 root 中是否包含和 subRoot 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
二叉树 tree 的一棵子树包括 tree 的某个节点和这个节点的所有后代节点。tree 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
示例 1:
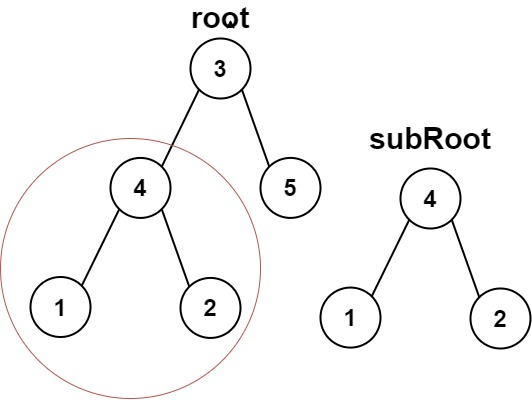
输入:root = [3,4,5,1,2], subRoot = [4,1,2]
输出:true
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
//相同的树
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
//结束条件
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
return true;
//结构上
if(p==NULL&&q!=NULL)
return false;
if(p!=NULL&&q==NULL)
return false;
if(p->val!=q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot) {
if(root == NULL)
return false;
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot))
return true;
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}
7.平衡二叉树
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是 平衡二叉树
示例 1:
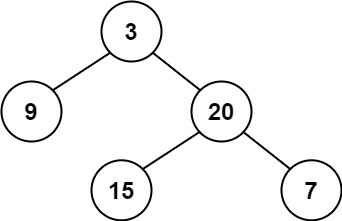
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:true
算法思路:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
// int TreeDepth(struct TreeNode* root)
// {
// if(root==NULL)
// return 0;
// int left = TreeDepth(root->left);
// int right = TreeDepth(root->right);
// return left>right?left+1:right+1;
// }
//最好是O(N),最坏是O(N*N) 重复计算子树的高度
// bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root) {
// if(root == NULL)
// return true;
// int leftDepth = TreeDepth(root->left);
// int rightDepth = TreeDepth(root->right);
// if(abs(leftDepth-rightDepth)>1)
// return false;
// return isBalanced(root->left)&&isBalanced(root->right);
// }
//法二:要求优化到最坏是O(N)
//后序,判断的同时带高度
bool _isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root,int* pDepth)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
*pDepth = 0;
return true;
}
int leftDepth = 0;
if(_isBalanced(root->left,&leftDepth) == false)
return false;
int rightDepth = 0;
if(_isBalanced(root->right,&rightDepth) == false)
return false;
if(abs(leftDepth-rightDepth)>1)
return false;
*pDepth = leftDepth>rightDepth?leftDepth+1:rightDepth+1;
return true;
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root) {
int depth = 0;
return _isBalanced(root,&depth);
}
8.给你一个字符串构建二叉树
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType _data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* _left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* _right;
}BTNode;
BTNode* CreateTree(char* str, int* pi)
{
if (str[*pi] == NULL)
{
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
else
{
BTNode* root = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
root->_data = str[*pi];
(*pi)++;
root->_left = CreateTree(str,pi);
root->_right = CreateTree(str,pi);
return root;
}
}
int main()
{
char str[100];//ab##c##
scanf("%s", str);
int i = 0;
BTNode* root = CreateTree(str, &i);
return 0;
}
9.二叉树第K层结点的个数
//分治思想,大问题化为若干类似小问题
int BTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
//k=1时侯 才是第k层
if (k == 1)
{
return 1;
}
return BTreeLevelKSize(root->_left, k - 1)
+ BTreeLevelKSize(root->_right, k - 1);
}
10.二叉树简单操作
//二叉树中查找x结点
BTNode* BTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x);
//二叉树销毁
void BTDestory(BTNode* root);
//二叉树层序遍历
void BTLevelOrder(BTNode* root);
//二叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* BTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
BTNode* node = BTreeFind(root->_left, x);
if (node)
{
return node;
}
BTNode* node = BTreeFind(root->_right, x);
if (node)
{
return node;
}
return NULL;;
}
void BTDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
BTDestory(root->_left);
BTDestory(root->_right);
free(root);
root = NULL;
}
//二叉树层次遍历
void BTLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
InitQueue(&q);
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%c ", front->_data);
if (front->_left)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->_left);
}
if (front->_right)
{
QueuePush(&q, front->_right);
}
}
QueueDestory(&q);
printf("\n");
}
11.判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
算法思路:
//判断是否是完全二叉树 在层次遍历基础上,当出现NULL结点时,判断队列是否有不为NULL结点存在
int BTComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
InitQueue(&q);
if (root == NULL) {
return 1;
}
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
//printf("%c ", front->_data);
if (front == NULL)
{
break;
}
QueuePush(&q, front->_left);
QueuePush(&q, front->_right);
}
//判断队列是否有非空结点存在
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front != NULL)
{
QueueDestory(&q);
return 0;
}
}
QueueDestory(&q);
printf("\n");
return 1;
}
堆

OJ
1.最小的k个数
设计一个算法,找出数组中最小的k个数。以任意顺序返回这k个数均可。
示例:
输入: arr = [1,3,5,7,2,4,6,8], k = 4
输出: [1,2,3,4]
算法思路:通过堆的特性,大根堆中父亲结点都是大于左右孩子结点,那么先选取数组中前K个元素建立拥有K个结点的大根堆,然后依次遍历剩下(N-K)个元素,通过与大根堆顶元素比较进行向下调整,如果该元素大于堆顶元素肯定不是要求K个数中之一(舍弃),如果该元素小于堆顶元素,把该元素赋值给堆顶元素,然后进行向下调整为大根堆,依次往下遍历数组,直到最后,那么此时堆中的K个结点即为所求最小K个数。
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
//堆排序 要实现递增建大根堆,实现递减建小根堆
//TopK 建拥有K个元素的堆, 找最小k个建大根堆,找最大k个建小根堆
int* smallestK(int* arr, int arrSize, int k, int* returnSize) {
//
*returnSize = k;
//开辟k个大小的数组
int* retArr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*k);
if(k<1)
return retArr;
for(int i = 0;i<k;i++)
{
retArr[i] = arr[i];
}
void AdjustDown(int* a,int n,int root)
{
int parent = root;
int child = parent*2+1;
while(child<n)
{
//找出最大的孩子
if(child+1<n && a[child]<a[child+1])
{
child++;
}
if(a[child]>a[parent])
{ //交换父子,大的为父
int tmp = a[child];
a[child] = a[parent];
a[parent] = tmp;
//继续向下调整
parent = child;
child = parent*2+1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//1.retArr建大根堆 根也要调整i>=0;
//初始从第一个非叶结点开始向下调整,左右孩子小于父亲结点
for(int i = (k-1-1)/2;i>=0;i--)
{
AdjustDown(retArr,k,i);
}
//2.遍历数组arr的元素与K堆顶进行比较(retArr[0])
//比堆顶小的元素做向下调整
for(int j = k;j<arrSize;j++)
{
if(arr[j]<retArr[0])
{
retArr[0] = arr[j];
AdjustDown(retArr,k,0);
}
}
return retArr;
}